Protecting Plants from Frost and Freezing Temperatures: A Comprehensive Guide
By: Woodys Admin
25 December, 2025
0 Comments
Protecting Plants from Frost and Freezing Temperatures: A Comprehensive Guide
As winter approaches, gardeners and farmers face the annual challenge of safeguarding their plants from frost and freezing temperatures. Frost can be a silent killer, causing irreversible damage to tender vegetation and leading to significant losses. Whether you're nurturing a small garden or managing a large agricultural operation, understanding how to protect your plants is crucial. In this guide, we’ll explore effective strategies to shield your plants from frost and freezing temperatures, helping you extend the growing season and preserve your green investments.

Understanding Frost and Its Impact on Plants
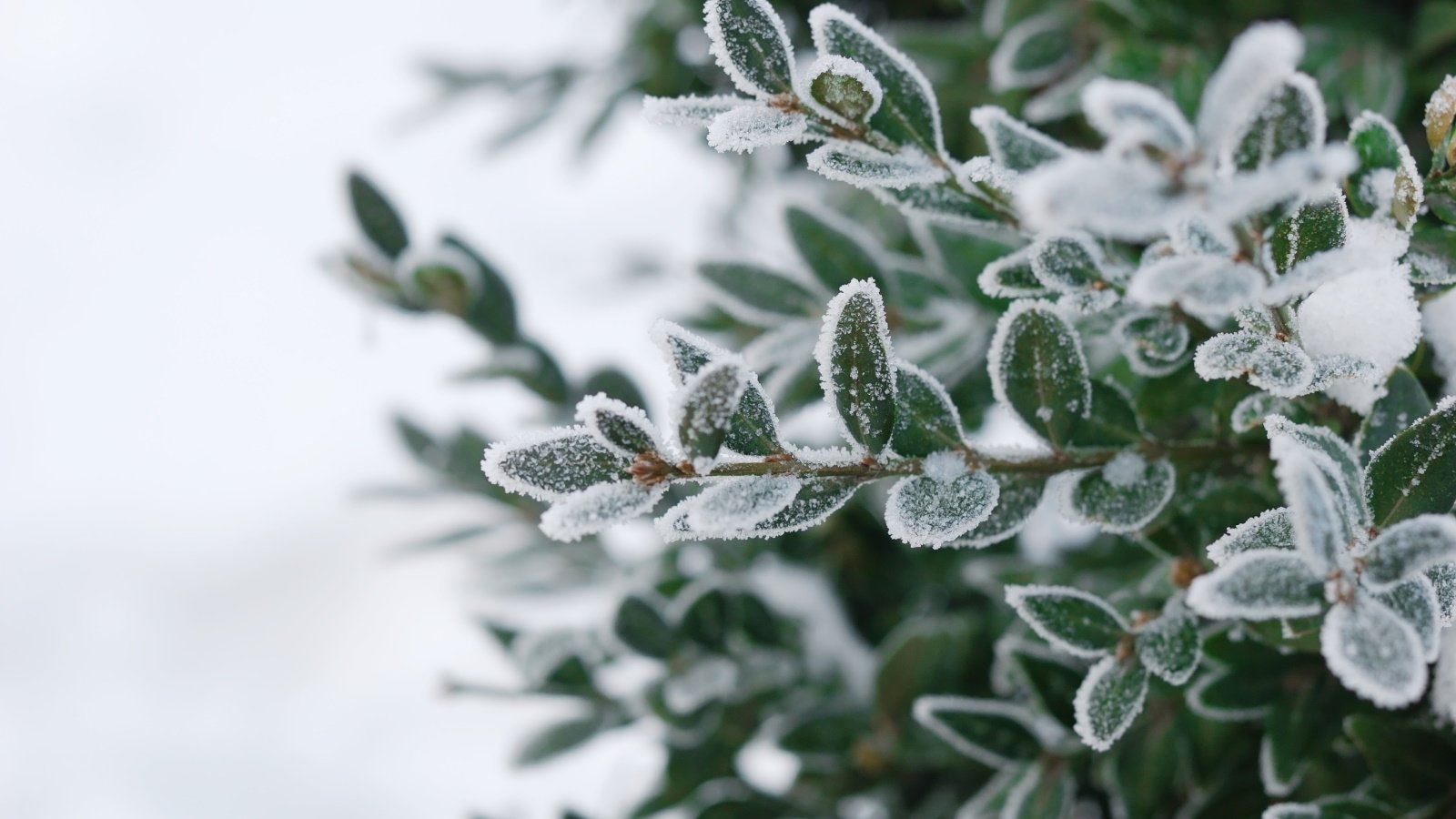
Frost occurs when temperatures drop to 32°F (0°C) or below, causing ice crystals to form on plant surfaces. This can lead to cell damage, wilting, and even plant death.
- The severity depends on the plant type, duration of exposure, and temperature intensity.
- Plants most vulnerable include tender vegetables (tomatoes, peppers), young seedlings, and flowering plants.
Predicting Frost: When and Why It Happens
Frost typically occurs on clear, calm nights when heat escapes the ground quickly. Key factors influencing frost formation include:
- Temperature: Below 32°F (0°C) for most plants.
- Humidity: High humidity increases frost risk.
- Wind: Calm conditions allow frost to settle.
- Soil Moisture: Dry soil retains less heat, increasing risk.
Use weather forecasts and frost prediction tools to stay ahead.
Methods to Protect Plants from Frost
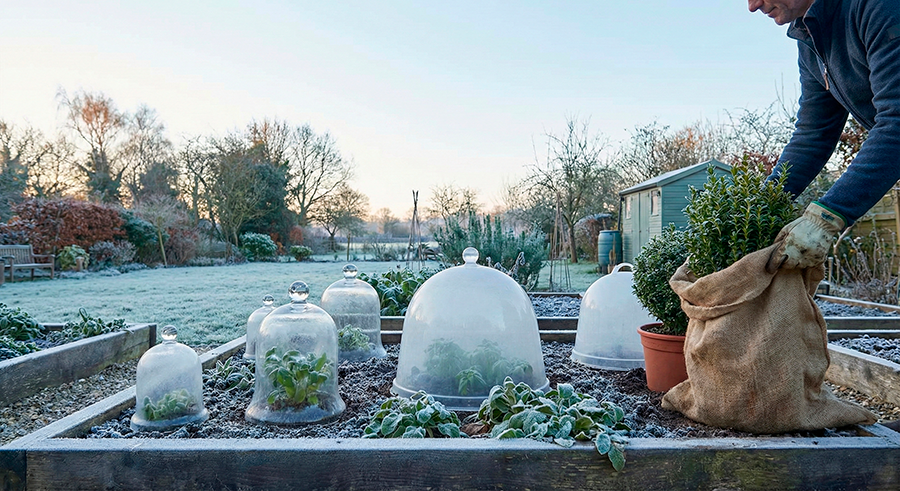
1. Covering Plants
- Blankets and Sheets: Use breathable fabrics like old sheets or frost cloths. Secure with stakes or rocks.
- Row Covers: Lightweight, breathable fabrics that trap heat while allowing light and water in.
- Plastic Covers: Effective but risk overheating during the day—remove during sunny hours.
2. Insulating with Mulch
- Apply a thick layer (3–4 inches) of organic mulch (straw, wood chips) around plants. This retains soil heat and protects roots.
3. Watering Strategies
- Water Before Frost: Moist soil retains heat better than dry soil. Water plants in the evening to leverage heat release.
- Drip Irrigation: Some systems can be used to spray water (not ideal for all plants, as ice can form).
4. Using Heat Sources
- Frost Clamps/Lights: Specialized devices that emit heat. Place carefully to avoid fire risks.
- LED Grow Lights: Can provide mild warmth, though not a primary solution.
5. Choose Resistant Varieties
- Plant frost-tolerant species or varieties bred for cooler climates. Examples include kale, spinach, and certain herbs.
6. Create a Microclimate
- Windbreaks: Plant trees or use barriers to block cold winds.
- Cold Frames/Hoop Houses: Trap heat during the day and retain it at night for extended protection.

Specific Strategies for Different Plants
- Vegetables: Cover tender crops like tomatoes and peppers. For root vegetables (carrots, beets), mulch heavily.
- Flowers: Use covers for delicate blooms. Move potted plants indoors if possible.
- Trees/Shrubs: Wrap trunks with burlap, and apply anti-desiccant sprays to evergreens.
Steps to Take Before, During, and After a Frost
- Before: Check forecasts, water plants, prepare covers.
- During: Cover plants in the evening, remove covers in the morning.
- After: Check for damage, remove dead parts, and adjust care.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Using Non-Breathable Covers: Can cause moisture buildup and damage.
- Forgetting to Remove Covers: Leads to overheating or trapped moisture.
- Inconsistent Watering: Keep soil moist but not waterlogged.
Technological Aids and Tools
Weather Stations: Monitor temperature and humidity.
Smart Irrigation Systems: Automate watering based on conditions.
Frost Alarms: Notify you when temperatures drop critically.
Conclusion
Protecting plants from frost requires preparation, vigilance, and the right techniques. By understanding the risks and implementing these strategies, you can minimize damage and enjoy a thriving garden year-round. Whether you’re a hobbyist or a professional, taking steps to shield your plants from freezing temperatures ensures they survive to flourish again.





Leave a Reply